Marketing dissertation writing stands as a pivotal academic task for any business student. Whether you’re pursuing a Bachelor’s, Master’s, or PhD degree, your dissertation marks the true culmination of your academic journey. It’s a complex undertaking that demands not only sharp analytical skills and robust research abilities but also refined academic writing prowess and, crucially, a profound understanding of marketing theories, contemporary strategies, and evolving market dynamics.
Indeed, marketing dissertation writing isn’t just about compiling pages of information or regurgitating textbook knowledge. It’s an intricate process of showcasing your deep understanding of multifaceted concepts like consumer behavior, the nuances of brand perception, the transformative power of digital evolution, and the pervasive influence of global business trends. More significantly, it’s about contributing original thought, fresh insights, and novel perspectives to the vast and ever-expanding academic world of marketing. This guide aims to be your definitive resource for successful marketing dissertation writing.
Table of Contents
The Indispensable Importance of Marketing Dissertation Writing
Engaging in marketing dissertation writing is essential for several compelling reasons, extending far beyond simply fulfilling a graduation requirement:
- Demonstrates Expertise and Application: A well-written marketing dissertation writing project serves as tangible proof of your ability to conduct thorough, systematic research. It shows you can apply complex marketing theories to real-life scenarios, analyze data critically, and synthesize findings into coherent, actionable insights. This capability is highly valued in both academic and professional spheres.
- Contributes to Academic Knowledge: Your work isn’t just for a grade; it has the potential to serve as a valuable reference point for future students, researchers, and practitioners. Original marketing dissertation writing can introduce new concepts, validate existing theories in new contexts, or even challenge conventional wisdom, thereby enriching the collective body of marketing knowledge.
- Boosts Career Prospects and Professional Credibility: In today’s competitive job market, a strong academic performance, particularly a distinguished dissertation, can significantly enhance your resumé. Recruiters and companies often value candidates who can demonstrate commitment, critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and the capacity for independent research—all qualities honed through rigorous marketing dissertation writing. It signals to potential employers that you can tackle complex challenges and contribute innovative solutions.
A Step-by-Step Process for Effective Marketing Dissertation Writing
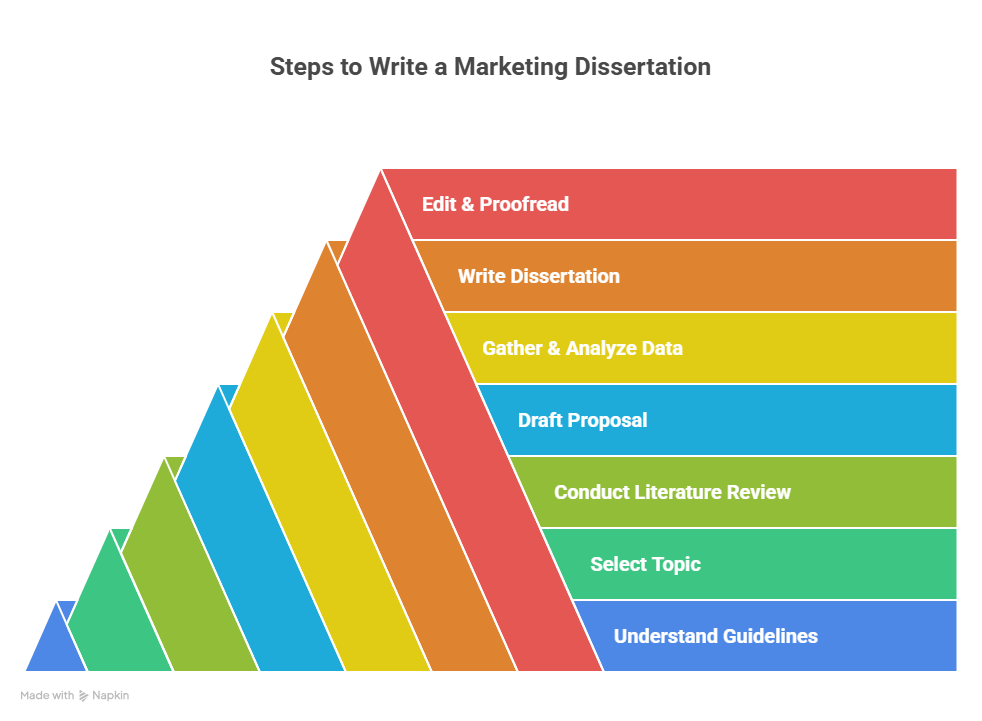
Approaching your dissertation efficiently and systematically is paramount. This marketing dissertation writing guide outlines a structured process to help you navigate each stage with clarity and purpose:
1. Understand Your University Guidelines – The Blueprint for Marketing Dissertation Writing
Before you even pick a topic, your first and most critical step in marketing dissertation writing is to thoroughly comprehend your institution’s specific dissertation manual. This document is your foundational blueprint.
- Read the manual meticulously: Pay close attention to every detail, including word limits for each chapter, required citation formats , structural requirements (e.g., specific headings, subheadings), submission deadlines, and ethical clearance procedures.
- Note down specifics: Create a checklist of all requirements to ensure compliance throughout your marketing dissertation writing Non-adherence to these guidelines can lead to delays or even rejection.
2. Select a Topic That Aligns with Your Interests – Fueling Your Marketing Dissertation Writing
Choosing a topic is arguably the most impactful decision in your marketing dissertation writing process. Your passion for the subject will be your primary motivator throughout the potentially arduous months ahead.
- Prioritize genuine interest: Pick something that truly fascinates you. This intrinsic motivation will sustain your enthusiasm when faced with challenges inherent in extensive marketing dissertation writing.
- Consider feasibility: Ensure your chosen topic is manageable within the given timeframe, considering data accessibility and available resources.
3. Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Review – The Foundation of Marketing Dissertation Writing
The literature review is more than just a summary of existing works; it’s a critical analysis that forms the intellectual backbone of your marketing dissertation writing.
- Analyze existing theories and research papers: Delve deeply into seminal works, contemporary research articles, and relevant theoretical frameworks within your chosen marketing domain. Understand the evolution of thought and key debates.
- Identify gaps and position your study: The core purpose is to identify what has already been researched, what theories exist, and, crucially, what questions remain unanswered. This allows you to effectively position your study, demonstrating its originality and significance within the existing academic discourse in marketing dissertation writing.
4. Draft a Robust Research Proposal – Your Marketing Dissertation Writing Blueprint
Your research proposal is a mini-dissertation in itself. It’s a compelling argument for why your research should be undertaken and serves as a roadmap for your entire marketing dissertation writing project.
- Key components: Clearly articulate your research questions, specific objectives, the proposed methodology (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed), and your expected outcomes or contributions.
- Supervisor approval: This is a mandatory step. Present your proposal to your supervisor for critical feedback and formal approval before proceeding with the main marketing dissertation writing.
5. Gather and Analyze Data – The Empirical Core of Marketing Dissertation Writing
This phase involves the systematic collection and interpretation of information to answer your research questions. It’s the empirical heart of your marketing dissertation writing.
- Choose appropriate methods: Decide whether a qualitative approach (e.g., in-depth interviews, focus groups, case studies) or a quantitative approach (e.g., surveys, experiments) best suits your research questions. Often, a mixed-methods approach combines both for a richer understanding.
- Utilize analytical tools: For quantitative data, tools like SPSS, R, Python (with libraries like Pandas or SciPy), or Excel are invaluable. For qualitative data, software like NVivo or Atlas.ti can aid in thematic analysis and coding. Accuracy in this phase is crucial for credible marketing dissertation writing.
7. Edit and Proofread Meticulously – The Final Polish for Marketing Dissertation Writing
This final stage is non-negotiable. Even the most brilliant research can be undermined by errors. Thorough editing and proofreading are essential to ensure your marketing dissertation writing is flawless.
- Check everything: Scrutinize grammar, punctuation, spelling, formatting consistency, and accurate referencing. A polished document reflects professionalism and attention to detail.
- Read aloud: This helps catch awkward phrasing or grammatical errors easily missed when reading silently.
Research Methodologies for Marketing Dissertation Writing
Choosing the right methodology is one of the most critical decisions in your marketing dissertation writing. It dictates how you will gather and analyze data to answer your research questions. You generally have three broad options:
Quantitative Methods
These methods focus on numerical data and statistical analysis to test hypotheses and establish relationships between variables. They are ideal when you want to measure, quantify, and generalize findings to a larger population.
- Surveys: Widely used in marketing dissertation writing for collecting data from a large number of respondents through questionnaires (online, mail, or in-person). They can be cross-sectional (at one point in time) or longitudinal (over a period).
- Questionnaires: The instrument used in surveys. Design is crucial for unbiased data.
- Experiments: Involve manipulating one or more independent variables to determine their effect on a dependent variable. Often used in marketing dissertation writing to test the effectiveness of advertising campaigns, pricing strategies, or product features in a controlled environment (e.g., A/B testing).
Ideal for: Statistical analysis, hypothesis testing, identifying trends, and making generalizations.
Qualitative Methods
These methods focus on exploring in-depth understanding, perceptions, and motivations, often involving non-numerical data. They are invaluable for gaining rich insights into complex phenomena that numbers alone cannot capture.
- Interviews: One-on-one, in-depth conversations with individuals to gather detailed insights into their experiences, opinions, and motivations. Can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
- Focus Groups: Group discussions (typically 6-10 participants) led by a moderator to explore perceptions, opinions, attitudes, and ideas about a specific product, service, or marketing concept.
Mixed Methods
This approach combines both quantitative and qualitative methods within a single study. It leverages the strengths of both approaches to provide a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the research problem. For instance, you might use surveys (quantitative) to identify general trends and then follow up with interviews (qualitative) to explore the reasons behind those trends. Many advanced marketing dissertation writing projects benefit from this integrated approach.
Structuring Your Marketing Dissertation: A Comprehensive Outline
A well-structured dissertation is crucial for clarity, coherence, and impact. While specific requirements may vary by institution, a typical structure for marketing dissertation writing includes the following key sections:
- Title Page: This includes your dissertation title, your name, institution, department, degree, and submission date. The title should be concise and accurately reflect your research.
- Abstract: This is a concise summary of your entire dissertation, typically 200–300 words. It should briefly state your research problem, methodology, key findings, and main conclusions. This is often the first, and sometimes only, section many readers will see, so it needs to be compelling and informative.
- Acknowledgments: A brief section where you express gratitude to individuals (supervisor, family, friends) and institutions who supported your marketing dissertation writing
Introduction
This chapter sets the stage for your entire marketing dissertation writing project.
- Background to the Study: Provide a broad overview of the marketing context relevant to your topic.
- Problem Statement: Clearly articulate the specific problem or gap in knowledge that your research aims to address. This is the “why” of your study.
- Research Questions and Objectives: State the specific questions your research will answer and the objectives you aim to achieve.
- Research Aims: A broader statement of what you intend to accomplish.
- Significance of the Study: Explain why your research is important, detailing its theoretical contributions to marketing knowledge and its practical implications for marketing professionals.
- Scope and Limitations: Define the boundaries of your study and acknowledge any constraints that might affect your findings.
- Dissertation Structure Overview: Briefly outline what each subsequent chapter will cover.
Literature Review
This is a critical, analytical survey of existing scholarly work relevant to your research. It’s more than just summarizing; it’s about critically evaluating and synthesizing.
- Theoretical Framework: Discuss the core theories and models from marketing and related fields that underpin your research.
- Conceptual Framework: Develop your own conceptual model illustrating the relationships between key variables in your study, based on the literature.
- Review of Key Themes/Concepts: Systematically discuss major research findings and debates related to your topic.
- Identification of Research Gaps: Pinpoint what is missing in current literature that your marketing dissertation writing will address.
- Hypotheses Development (if applicable): Formulate testable hypotheses based on the identified gaps and theoretical support.
Methodology
This chapter rigorously details how you conducted your research. It must be sufficiently detailed for another researcher to replicate your study.
- Research Philosophy/Paradigm: Discuss your epistemological and ontological stances (e.g., positivism, interpretivism).
- Research Approach: Explain whether your study is deductive (testing theory) or inductive (developing theory).
- Research Design: Detail your overall research strategy (e.g., survey, experimental, case study, ethnography).
- Population and Sample: Describe your target population and the sampling technique used (e.g., random, convenience, purposive), along with sample size justification.
- Data Collection Methods: Detail the specific instruments and procedures used to collect data (e.g., questionnaire design, interview protocol, experimental setup).
- Data Analysis Methods: Explain how you analyzed your data (e.g., statistical tests, thematic analysis, discourse analysis).
- Validity, Reliability, and Generalizability/Trustworthiness: Discuss how you ensured the quality and rigor of your research.
- Ethical Considerations: Outline the ethical principles adhered to (e.g., informed consent, anonymity, confidentiality).
Data Analysis and Results
This chapter presents your findings objectively, without interpretation.
- Data Presentation: Use tables, graphs, and descriptive statistics to present your raw data and preliminary findings.
- Results of Analysis: Detail the outcomes of your statistical tests (for quantitative research) or the main themes and categories identified (for qualitative research).
- Answer Research Questions (Directly): Present the findings in relation to your research questions and hypotheses.
Discussion
This is where you interpret your results, compare them with existing literature, and discuss their implications.
- Interpretation of Findings: Explain what your results mean in the context of your research questions.
- Comparison with Literature: Discuss how your findings align with, contradict, or expand upon existing research discussed in your literature review.
- Theoretical Implications: How does your research contribute to marketing theory? Does it support, refute, or modify existing models?
- Managerial/Practical Implications: How can your findings be applied by marketing practitioners, businesses, or policymakers?
- Limitations of the Study: Acknowledge any constraints or weaknesses in your research design or execution.
Conclusion and Recommendations
This chapter summarizes your entire marketing dissertation writing journey and looks forward.
- Summary of Key Findings: Briefly reiterate the most important results and conclusions.
- Original Contribution: Clearly state what new knowledge your dissertation has added to the field of marketing.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Suggest avenues for further study based on your limitations and unanswered questions.
- Concluding Remarks: A powerful final statement that reinforces the overall impact of your work.
- References/Bibliography: A comprehensive and accurately formatted list of all sources cited in your dissertation.
- Appendices: Include supplementary materials that support your research but aren’t essential for the main body (e.g., survey forms, interview transcripts, detailed statistical outputs, ethical approval letters).
Expert Tips to Drastically Improve the Quality of Your Marketing Dissertation Writing
Achieving excellence in marketing dissertation writing requires strategic effort and attention to detail.
- Use Credible and Diverse Sources: Always cite from highly reputable academic journals (e.g., Journal of Marketing, Journal of Consumer Research, Harvard Business Review, Marketing Science, Journal of Advertising), peer-reviewed conference papers, and authoritative books. Avoid relying heavily on popular press articles or non-academic websites.
- Maintain Objectivity and Academic Rigor: Avoid biased statements or emotional language. Let your data and evidence speak for themselves. Present findings dispassionately and interpret them critically, a core tenet of robust marketing dissertation writing.
- Adhere to Academic Style and Tone: Use formal, precise, and unambiguous language. Maintain a third-person perspective and avoid colloquialisms. Clarity, conciseness, and logical argumentation are paramount in marketing dissertation writing.
- Prioritize Originality and Avoid Plagiarism: Ensure every idea, finding, or piece of data that isn’t your own original thought is properly cited. Use reputable plagiarism detection tools like Turnitin or Grammarly Premium’s plagiarism checker to identify and rectify any accidental instances before submission.
- Seek and Incorporate Feedback: Don’t work in isolation. Actively solicit feedback from your supervisor, academic peers, and even professional editors or mentors throughout the marketing dissertation writing Be open to constructive criticism and make necessary revisions.
Marketing Dissertation Writing Services: When & Why to Use Them
Even with the best intentions and diligent effort, marketing dissertation writing can become an overwhelming task. This is where professional services can provide substantial, ethical support for students grappling with various challenges.
Students often seek external support due to:
- Severe Time Constraints: Juggling multiple responsibilities makes it nearly impossible to dedicate the required hours to in-depth marketing dissertation writing.
- Language Difficulties: Non-native English speakers may struggle with academic English, grammar, and nuanced expression.
- Conceptual Clarity Issues: Difficulty in grasping complex marketing theories or articulating abstract concepts effectively.
- Methodological Challenges: Uncertainty about choosing the right research design, executing data collection, or performing advanced statistical/qualitative analysis.
- Writer’s Block: Periods of mental stagnation where putting thoughts onto paper seems impossible.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do I choose the best topic for my marketing dissertation?
PhDiZone recommends selecting a topic that aligns with your academic interests and industry relevance. Consider emerging trends in digital marketing, consumer behavior, or branding, and always ensure that your topic is researchable and supervisor-approved.
2. Can I use secondary data for my dissertation?
Yes, using secondary data is entirely acceptable—especially when conducting literature reviews, case studies, or market evaluations. PhDiZone ensures that all secondary sources we recommend or analyze are credible, recent, and academically sound.
3. Is it ethical to use a dissertation writing service like PhDiZone?
Absolutely. PhDiZone operates under strict academic ethics, providing support through mentoring, editing, formatting, plagiarism checks, and research structuring. We never offer ghostwriting—we empower students to build their academic capability.
4. How long should my marketing dissertation be?
Typically, a marketing dissertation for a Master’s program should range between 8,000 to 20,000 words. PhDiZone helps you maintain the required depth, clarity, and structure no matter the length, ensuring academic excellence throughout.
5. What tools can help me write a better dissertation?
PhDiZone recommends tools such as Grammarly for proofreading, Zotero or Mendeley for citation management, and SPSS or NVivo for data analysis. We also provide technical training and hands-on assistance in using these tools effectively for your marketing research.
Conclusion:
Marketing dissertation writing is undeniably a rigorous academic endeavor that tests your research, analytical, and writing capabilities to their fullest. However, with the right strategic approach, meticulous planning, and professional assistance when needed, it can be an incredibly rewarding and transformative process. It’s an opportunity to delve deep into an area of marketing that truly interests you and to make a tangible contribution to the field.
Whether you’re meticulously delving into the intricacies of digital marketing, unraveling the complexities of consumer psychology, or strategically exploring the dynamics of brand management, make sure your marketing dissertation writing reflects originality, unwavering clarity, and undeniable relevance to today’s rapidly evolving business landscape. Stay focused, remain organized, and always remember—your dissertation is not just a requirement; it’s your unique opportunity to contribute meaningfully to the marketing world and establish yourself as an emerging expert.