In the evolving research landscape, qualitative data analysis services play a critical role in interpreting non-numerical data, providing deeper insights into human experiences, opinions, and behaviors. Unlike quantitative analysis, which focuses on numerical data, qualitative analysis examines textual, audio, or visual data to identify patterns and themes.
Researchers, businesses, and academic institutions rely on qualitative data analysis services to derive meaningful conclusions from complex datasets. Choosing the right method is crucial for ensuring accuracy, reliability, and impactful findings. This article explores the best qualitative data analysis methods, their processes, applications, and best practices for research excellence.
Table of Contents
What Is Qualitative Data Analysis?
Qualitative data analysis is the systematic examination of non-numeric data collected from interviews, surveys, focus groups, observations, and textual sources. The goal is to extract themes, meanings, and insights that inform decision-making, policy development, and academic research.
A professional qualitative data analysis service provides expertise in structuring data, identifying key trends, and ensuring credibility in research findings. These services are widely used in healthcare, education, marketing, social sciences, and business research.
Top 10 Methods of Qualitative Data Analysis
1. Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is one of the most widely used qualitative data analysis service methods, focusing on identifying recurring themes or patterns in textual, visual, or audio data. It helps researchers make sense of large volumes of unstructured information by categorizing data into meaningful themes.
-
Process:
- Familiarizing with the data by reading or listening to content multiple times
- Systematically coding significant words, phrases, and expressions
- Identifying patterns and organizing codes into broader themes
- Reviewing and refining themes to ensure relevance and accuracy
- Producing a final report with supporting data extracts
-
Applications:
- Used in market research to understand customer preferences and feedback
- Helpful in educational studies for analyzing student experiences
- Common in healthcare research for evaluating patient feedback and healthcare provider interactions
-
Advantages:
- Offers flexibility as it can be applied across multiple research fields
- Helps simplify complex datasets into well-structured themes
- Allows researchers to derive deep insights without numerical data
2. Grounded Theory
Grounded theory is an inductive qualitative data analysis service for research method that develops theories directly from collected data rather than relying on existing theories. It is particularly useful in exploratory studies where researchers seek to build new conceptual frameworks.
-
Process:
- Open coding: Identifying key points and labeling significant concepts
- Axial coding: Establishing relationships between different data points
- Selective coding: Refining codes into a central theme or theory
- Constant comparison: Continuously refining categories as new data emerges
- Theoretical saturation: Stopping data collection when no new insights appear
-
Applications:
- Useful in psychological research to understand emotional responses
- Applied in business studies to explore consumer behavior patterns
- Used in social sciences to study human interactions and communication
-
Advantages:
- Helps generate new theories that are data-driven and unbiased
- Encourages iterative analysis, making findings more reliable
- Provides in-depth understanding of complex social behaviors
3. Content Analysis
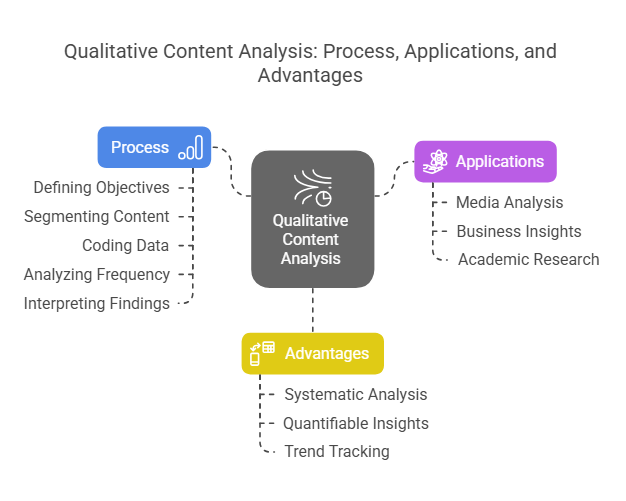
Content analysis is a qualitative method that involves systematically categorizing and interpreting text, images, or audio to identify patterns, trends, and meanings. It is commonly used in media studies, communication research, and social sciences.
- Process:
-
- Defining research objectives and selecting data sources
- Segmenting textual or visual content into meaningful categories
- Coding data using predefined or emergent categories
- Analyzing frequency and context of words, phrases, or symbols
- Interpreting findings to draw meaningful conclusions
-
Applications:
- Used in media analysis to study news coverage, advertisements, and social media trends
- Helps businesses monitor brand sentiment and customer perception
- Supports academic research on cultural and societal changes
-
Advantages:
- Enables systematic and objective analysis of large volumes of data
- Provides quantifiable insights into qualitative datasets
- Helps track communication trends over time
4. Narrative Analysis
Narrative qualitative data analysis service focuses on examining stories, interviews, and personal narratives to understand how individuals construct meaning from experiences. It is widely used in psychology, sociology, and literature studies.
-
Process:
- Gathering personal narratives through interviews or case studies
- Identifying story structure, themes, and character roles
- Analyzing emotions, language, and cultural context
- Interpreting how narratives shape individual or group identities
- Reporting findings through thematic storytelling
-
Applications:
- Helps psychologists understand trauma recovery and mental health conditions
- Used in education to explore student experiences and learning challenges
- Supports business branding through consumer storytelling
-
Advantages:
- Captures personal and emotional aspects of human experiences
- Provides deep insights into cultural and social perspectives
- Enhances understanding of identity formation and self-expression
5. Discourse Analysis
Discourse qualitative data analysis service examines how language, speech, and written text shape social and cultural realities. It is used to analyze political speeches, advertisements, media texts, and social interactions.
-
Process:
- Identifying key communication patterns and language use
- Examining power structures, ideologies, and social influence
- Comparing discourse across different contexts and timeframes
- Interpreting the impact of language on public perception and behavior
- Presenting findings with contextual references
-
Applications:
- Used in political science to analyze government speeches and policies
- Helps businesses refine marketing strategies by studying consumer discourse
- Supports media research by analyzing news narratives and biases
-
Advantages:
- Helps uncover hidden meanings behind words and expressions
- Useful for understanding public opinion and social change
- Enhances critical thinking about communication and influence
6. Phenomenological Analysis
Phenomenological analysis focuses on understanding people’s lived experiences and the meanings they attach to them. It is widely used in psychology, healthcare, and education.
-
Process:
- Bracketing: Setting aside researcher biases and assumptions
- Collecting in-depth interviews or first-person accounts
- Identifying significant statements and extracting themes
- Structuring findings into a comprehensive understanding of experiences
- Reporting narratives to highlight key insights
-
Applications:
- Used in medical research to explore patient experiences with chronic illness
- Helps educators understand students’ learning journeys and challenges
- Supports social work research on marginalized communities
-
Advantages:
- Provides a deep exploration of personal experiences
- Captures emotions, thoughts, and perspectives authentically
- Offers valuable insights for healthcare and therapy interventions
7. Framework Analysis
Framework qualitative data analysis service is a structured qualitative data analysis service method that helps systematically analyze data by categorizing it into themes based on a predefined framework. It is widely used in policy research, healthcare, and social sciences.
-
Process:
- Familiarizing with the data through repeated reading or listening
- Developing a thematic framework based on research objectives
- Indexing and coding data according to framework categories
- Charting key findings into structured matrices
- Interpreting results to generate meaningful conclusions
-
Applications:
- Used in public health research to analyze healthcare policies and patient care data
- Supports government and organizational policy analysis
- Helps in educational research by studying student feedback and learning outcomes
-
Advantages:
- Provides a structured and transparent approach to data analysis
- Allows for comparisons across different datasets
- Enhances research credibility through systematic categorization
8. Case Study Analysis
Case study analysis is a qualitative method that involves an in-depth examination of a single case, event, organization, or individual to understand complex phenomena. It is widely used in business, law, education, and medical research.
-
Process:
- Selecting a case based on research objectives
- Collecting detailed qualitative data through interviews, observations, and documents
- Analyzing the case within its real-life context
- Identifying patterns, relationships, and key insights
- Presenting findings through detailed case reports
-
Applications:
- Used in business studies to analyze company strategies and market trends
- Helps in legal research by examining landmark cases and judicial decisions
- Supports medical research through in-depth patient case studies
-
Advantages:
- Provides a deep and holistic understanding of real-world scenarios
- Allows researchers to explore contextual factors affecting the case
- Supports evidence-based decision-making in various industries
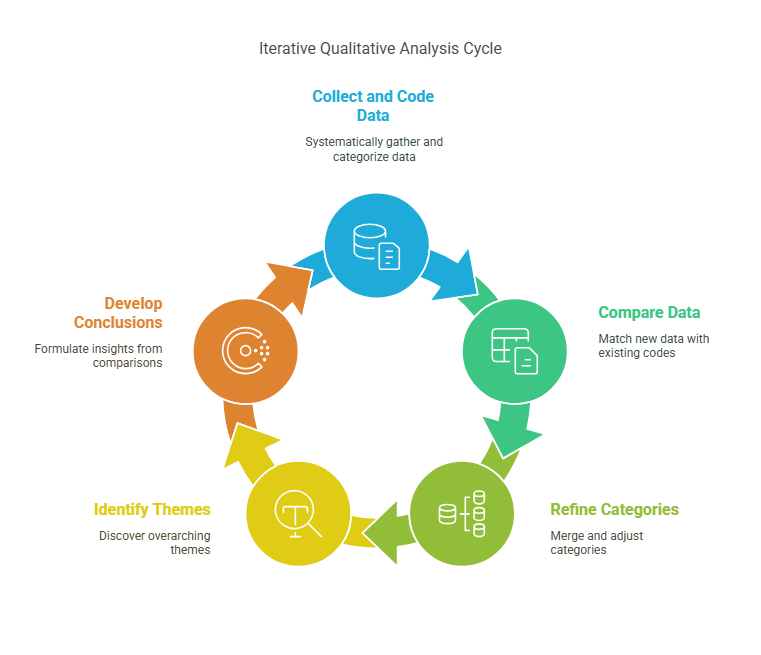
9. Constant Comparative Method
The constant comparative method is a qualitative research technique used in grounded theory studies, where data is continuously compared to identify emerging themes and categories.
-
Process:
- Collecting and coding qualitative data systematically
- Comparing new data with existing coded data
- Refining and merging categories as patterns emerge
- Identifying overarching themes and core theoretical concepts
- Developing conclusions based on iterative comparisons
-
Applications:
- Used in sociology and psychology to study social behavior patterns
- Helps businesses refine customer feedback analysis for product improvements
- Supports educational research by examining teaching methodologies and learning experiences
-
Advantages:
- Ensures a rigorous and iterative approach to qualitative analysis
- Helps refine emerging theories with continuous data validation
- Improves research accuracy through systematic data comparison
10. Action Research
Action research is a participatory method that involves researchers actively engaging with a community or organization to solve real-world problems while simultaneously studying the process.
-
Process:
- Identifying a practical issue that requires intervention
- Collaborating with stakeholders to collect qualitative data
- Implementing change or intervention strategies
- Observing and analyzing the effects of the intervention
- Reflecting on outcomes and refining the approach for continuous improvement
-
Applications:
- Used in education to develop new teaching strategies and improve student outcomes
- Helps organizations enhance workplace policies through participatory research
- Supports social work research by addressing community challenges
-
Advantages:
- Encourages collaboration and stakeholder involvement
- Leads to practical solutions that directly benefit communities and organizations
- Promotes continuous learning and adaptive research strategies
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is qualitative data analysis service, and why is it important?
Qualitative data analysis service involves systematically examining non-numeric data to extract patterns, themes, and insights. It is crucial for understanding human experiences, behaviors, and decision-making processes, making it valuable for research, business, healthcare, and social sciences.
2. What are the most commonly used qualitative data analysis service methods?
The most common methods include thematic analysis, grounded theory, content analysis, narrative analysis, discourse analysis, framework analysis, case study analysis, constant comparative method, and action research. Each method is chosen based on research goals and data type.
3. How can businesses benefit from qualitative data analysis services?
Businesses use qualitative data analysis services to understand customer preferences, brand perception, and market trends. It helps in developing effective marketing strategies, improving customer experience, and making data-driven decisions.
4. What industries use qualitative data analysis?
Industries such as healthcare, education, marketing, social sciences, public policy, and business research extensively use qualitative data analysis service to gain deep insights into complex human interactions.
5. What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative data analysis service?
Qualitative analysis focuses on non-numerical data, exploring themes and subjective meanings, while quantitative analysis deals with numerical data and statistical measurements. Qualitative research provides in-depth insights, whereas quantitative research offers measurable results.
6. How long does qualitative data analysis services take?
The time required depends on the complexity, data volume, and chosen method. A small-scale analysis may take a few weeks, while in-depth research projects can take months to complete.
7. How do qualitative data analysis services ensure research accuracy?
Professional services use structured methodologies, multiple coding techniques, peer validation, and software tools like NVivo and ATLAS.ti to enhance accuracy, credibility, and reliability of research findings.