In academic research, review articles are a vital resource for synthesizing and analyzing the existing body of knowledge on a particular topic. These reviews serve to summarize what is already known, identify emerging trends, and guide future research efforts. By evaluating existing literature, researchers can also uncover gaps in knowledge and suggest areas that require further investigation.
There are various types of research reviews, each with a unique methodological approach to gathering, analyzing, and synthesizing evidence. In this article, we will delve into the different types of research reviews, explaining their distinct characteristics and methodologies.
Table of Contents
1. Systematic Review
A systematic review is one of the most rigorous and structured approaches to synthesizing evidence. The goal of this type of review is to answer a specific research question by rigorously identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing all available studies on the topic. It follows a predefined and replicable methodology, which includes conducting a comprehensive search of the literature, applying inclusion/exclusion criteria to select studies, and critically assessing the quality of each study.
Key Features of Systematic Review:
-
Uses a structured and transparent methodology.
-
Aims to minimize bias and provide reproducible results.
-
Focuses on answering a specific research question.
-
Often includes a quality assessment of the studies included.
The systematic types of research reviews is particularly valuable when researchers want to provide a comprehensive and unbiased synthesis of a particular field or research question. It is widely used in fields such as healthcare, education, and social sciences, where high-quality evidence is crucial for making informed decisions.
2. Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical technique often employed within a systematic review. It involves the quantitative combination of results from multiple studies to produce a single estimate of the effect or outcome. By pooling data from various studies, this types of research reviews meta-analysis increases the statistical power and reliability of the results, helping to resolve inconsistencies between individual studies and providing more robust conclusions.
Key Features of Meta-Analysis:
-
Uses statistical methods to combine data from multiple studies.
-
Increases the statistical power by pooling data.
-
Resolves inconsistencies in individual study results.
Meta-analysis is particularly useful when studies report conflicting results on the same research question. By aggregating data from different studies, the types of research reviews can offer a clearer picture of the overall effect or trend.
3. Narrative Review (Traditional Review)
A narrative review, also known as a traditional review, is a more flexible and less structured form of review. Unlike systematic reviews, narrative reviews do not follow a rigid methodology and are often more qualitative in nature. The author of a narrative review typically provides a broad, descriptive summary of the literature on a particular topic, reflecting their perspective and expertise.
Key Features of Narrative Review:
-
More flexible and less structured than systematic reviews.
-
Offers a broad, descriptive summary of literature.
-
Reflects the author’s perspective on the topic.
Narrative reviews are valuable when the goal is to provide a general overview of a topic or when the research question is broad and does not require a systematic approach. However, the lack of a structured methodology means that narrative reviews are more susceptible to bias and subjectivity.
4. Scoping Review
A scoping review is designed to map the key concepts, types of evidence, and research gaps in a particular field. It is broader in scope than a systematic review and aims to provide an overview of the breadth and range of available literature on a topic. Unlike systematic types of research reviews, scoping reviews do not typically assess the quality of the included studies but focus on mapping the evidence and identifying areas where more research is needed.
Key Features of Scoping Review:
-
Broader in scope than systematic reviews.
-
Maps key concepts and identifies research gaps.
-
Does not assess the quality of the studies included.
Scoping reviews are particularly useful when there is limited information on a topic, or when researchers are looking to map the landscape of research in a particular area.
5. Critical Review
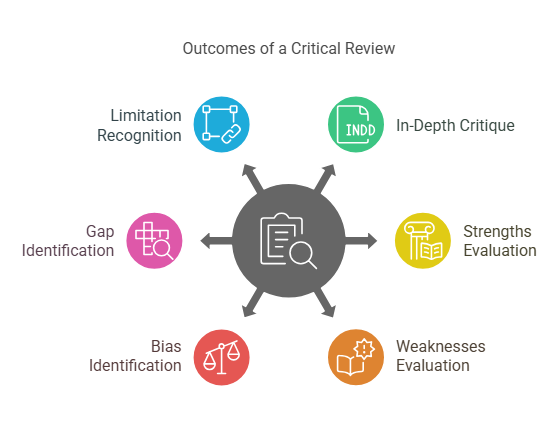
A critical review goes beyond simply summarizing existing research. It involves a critical evaluation of the strengths, weaknesses, methodologies, and findings of the studies under review. The aim of a critical review is to provide a deeper understanding of the literature, often by identifying biases, gaps in knowledge, and limitations in the studies reviewed. This types of research reviews is particularly useful when researchers want to challenge existing paradigms or suggest new avenues for future research.
Key Features of Critical Review:
-
Offers an in-depth critique of the literature.
-
Evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of individual studies.
-
Identifies biases, gaps, and limitations in the existing research.
Critical reviews are highly valuable for advancing knowledge by challenging existing conclusions and offering new perspectives on a research topic.
6. Rapid Review
A rapid review is an expedited form of a systematic review. It is conducted with limited resources or within a short time frame, focusing on providing a synthesis of the best available evidence as quickly as possible. While rapid types of research reviews follow a systematic process, they are often more selective in terms of study inclusion and have a streamlined approach to searching and analyzing the literature.
Key Features of Rapid Review:
-
Conducted quickly with limited resources.
-
Provides a synthesis of the best available evidence in a short time.
-
Often used for urgent policy or decision-making purposes.
Rapid reviews are commonly used when there is a need for timely evidence, such as in healthcare or policy-making scenarios where decisions need to be made quickly.
7. Umbrella Review (Overview of Reviews)
An umbrella review is a higher-level review that synthesizes multiple systematic reviews or meta-analyses on a specific topic. This types of research reviews aims to provide a consolidated summary of the evidence from a variety of reviews, highlighting overall trends, common conclusions, and any contradictions in the findings.
Key Features of Umbrella Review:
-
Synthesizes multiple systematic reviews or meta-analyses.
-
Provides a higher-level summary of existing evidence.
-
Highlights trends, contradictions, and overall conclusions.
Umbrella reviews are useful for obtaining a broad, consolidated view of the evidence on a particular topic, especially when multiple reviews or meta-analyses have been published.
8. Integrative Review
An integrative review combines both qualitative and quantitative research into a single synthesis. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of a topic by integrating various study designs, including theoretical and empirical research. The goal is to offer a more holistic view of a phenomenon by drawing on evidence from different methodologies.
Key Features of Integrative Review:
-
Combines both qualitative and quantitative research.
-
Provides a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
-
Integrates diverse types of research designs.
Integrative reviews are particularly valuable when researchers want to develop a holistic view of a complex topic that cannot be understood through a single methodology alone.
9. Critical Interpretive Synthesis
A critical interpretive synthesis focuses on synthesizing qualitative research. It goes beyond summarization by interpreting and integrating the findings of qualitative studies. This types of research reviews explores themes, concepts, and theoretical frameworks and often involves developing new theories or conceptual models based on the synthesis of the research.
Key Features of Critical Interpretive Synthesis:
-
Focuses on synthesizing qualitative research.
-
Interprets themes, concepts, and theoretical frameworks.
-
Develops new theories or models based on the synthesis.
This types of research reviews is particularly useful when the goal is to develop new theoretical insights or frameworks based on qualitative data.
10. State-of-the-Art Review
A state-of-the-art review provides an up-to-date overview of the latest developments in a specific area of research. It highlights the most current knowledge, technological advancements, or methodologies and often includes emerging trends and recent breakthroughs in the field. State-of-the-art types of research reviews are valuable for staying informed about cutting-edge research and identifying the latest innovations.
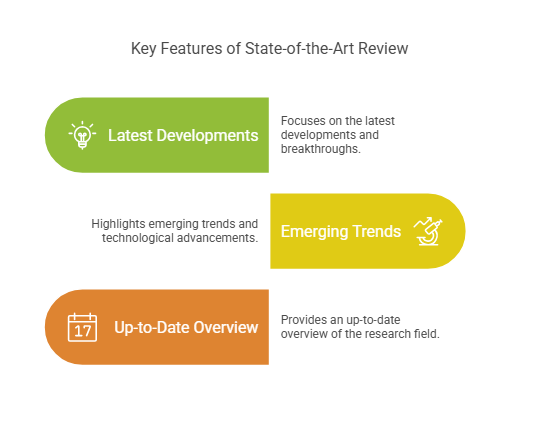
Key Features of State-of-the-Art Review:
-
Focuses on the latest developments and breakthroughs.
-
Highlights emerging trends and technological advancements.
-
Provides an up-to-date overview of the research field.
State-of-the-art types of research reviews are important for keeping researchers, practitioners, and policymakers informed about the most current and relevant advancements in their fields.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between a systematic review and a narrative review?
A systematic review follows a structured, predefined methodology to rigorously synthesize available evidence, while a narrative review provides a broad, descriptive summary of the literature, often reflecting the author’s perspective.
2. When should a meta-analysis be used?
A meta-analysis is typically used within a systematic types of research reviews to quantitatively combine results from multiple studies, providing a more reliable estimate of the effect or outcome.
3. What is the purpose of a scoping review?
A scoping review is used to map key concepts, types of evidence, and research gaps in a field, providing a broader overview of the literature without assessing study quality.
4. How does a critical review differ from other types of reviews?
A critical review goes beyond summarizing the literature by providing a deep analysis of study strengths, weaknesses, biases, and research gaps.
5. What is an umbrella review?
An umbrella review synthesizes multiple systematic reviews or meta-analyses on a specific topic, offering a higher-level summary of the evidence.
Conclusion
Each types of research reviews has its own methodology and purpose, making it essential for researchers to choose the appropriate review type based on their research question, available evidence, and intended outcome. Whether it’s synthesizing quantitative data through a meta-analysis, critically evaluating the literature with a critical review, or providing an overview of emerging trends in a state-of-the-art review, these different types of research reviews serve to advance knowledge in a field.
At PhDiZone, we specialize in guiding researchers through the complexities of academic writing, ensuring the selection and execution of the right review methodology to strengthen their research. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each types of research reviews, researchers can make informed decisions that will help guide future investigations and contribute to the broader academic discourse.